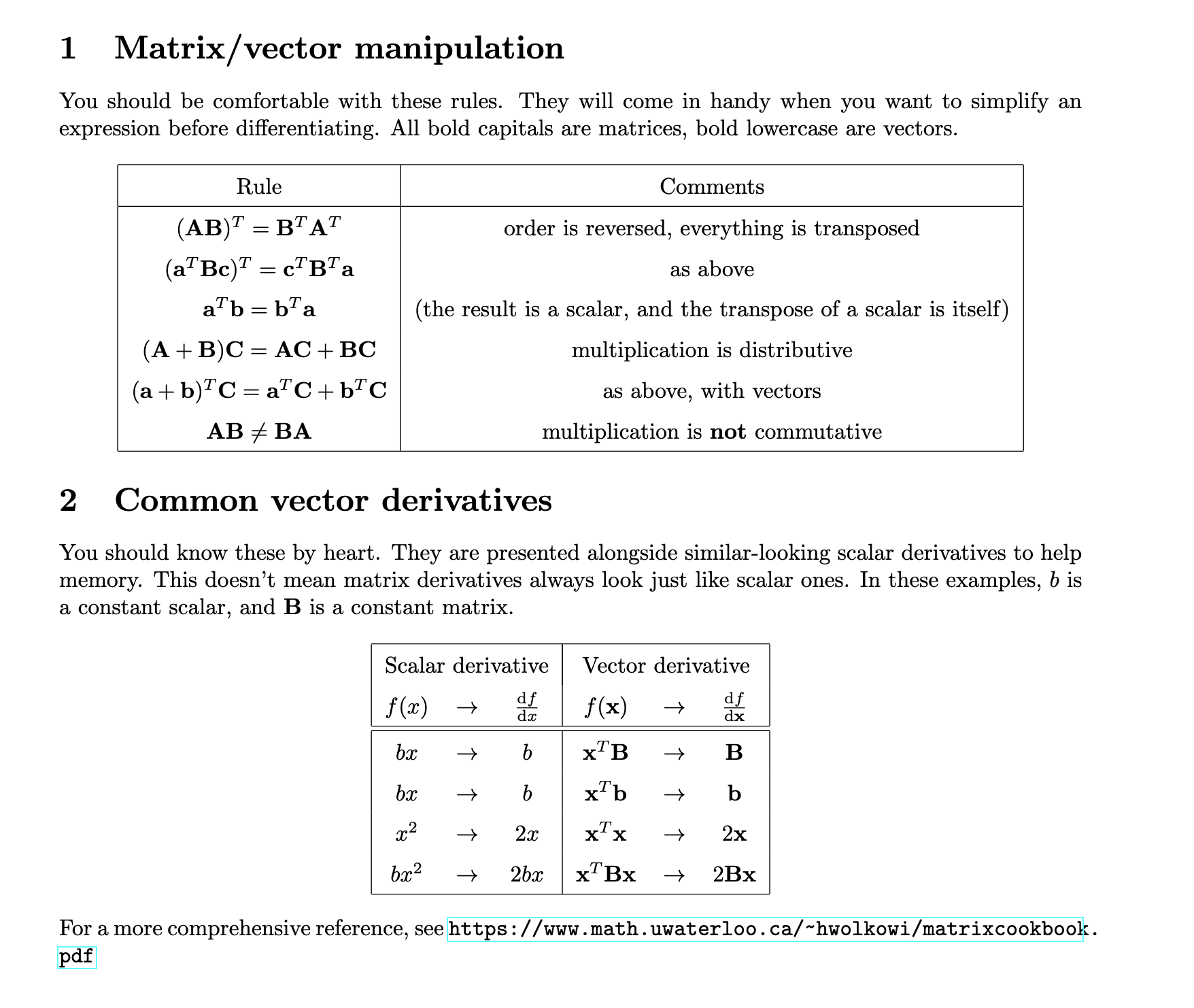
Transpose Rules
- \(\qty(AB)^{T} = B^{T}A^{T}\)
- \(\qty(a^{T}Bc)^{T} = c^{T} B^{T}a\)
- \(a^{T}b = b^{T}a\)
- \(\qty(A+B)C = AC + BC\)
- \(\qty(a+b)^{T}C = a^{T}C + b^{T}C\)
- \(AB \neq BA\)
Derivative
| Scalar derivative | Vector derivative |
|---|---|
| \(f\qty(x) \to \pdv{f}{x}\) | \(f\qty(x) \to \pdv{f}{x}\) |
| \(bx \to b\) | \(x^{T}B \to B\) |
| \(bx \to b\) | \(x^{T}b \to b\) |
| \(x^{2} \to 2x\) | \(x^{T}x \to 2x\) |
| \(bx^{2} \to 2bx\) | \(x^{T}Bx \to 2Bx\) |
Products
\begin{equation} \pdv{AB}{A} = B^{T}, \pdv{AB}{B} = A^{T} \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \pdv{Ax}{A} = x^{T}, \pdv{Ax}{x}= A \end{equation}
Vector and Quadratic Forms
\begin{equation} \pdv{y^{T} x}{x} = y, \pdv{y^{T} x}{y} = x \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \pdv{x^{T}Ax}{x} = \qty(A+A^{T})x = 2Ax \end{equation}
for symmetric A
Chain Rule for Matrix Multiplication
Suppose:
\begin{equation} z = Wu + b \end{equation}
\begin{equation} J = J\qty(z) \end{equation}
then: \(\pdv{J}{W} = \pdv{J}{z} u^{T}\).
Rest of them