CMU-15445 SEP042024
Last edited: August 8, 2025Disk based architecture
- the DBMS primarily stores stuff on non-violatle disk
- meaning: the DBMS’ job is to move stuff between violatle and non-volatle storage
Challenges
- how do you makue sure memory-writtten info is commited to disk?
Hierarchy model
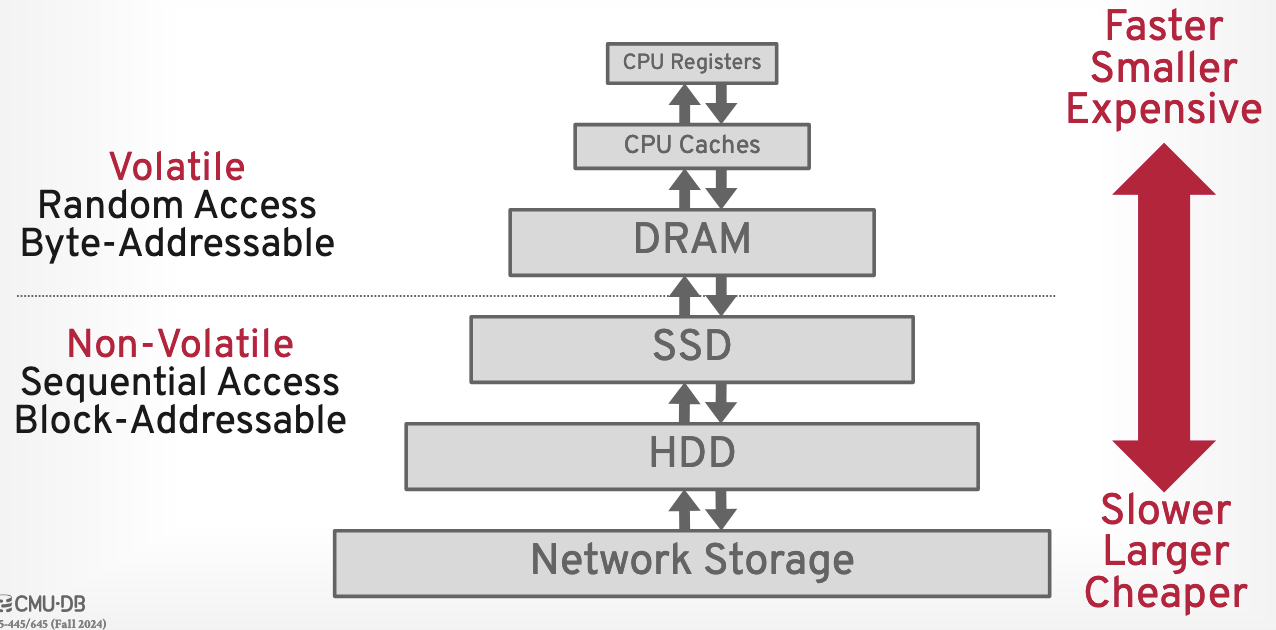
there’s a tradeoff because as your system because faster, you have less of it and (in case its volatle) it stays around less long
Access Order
Key challenge: random-access on non-volatile storage is almost always slower than sequential access
CNS regulation
Last edited: August 8, 2025A brain signal to help maintain glucose homeostatis
Brain takes glucose product + glucose uptake to control energy balance in food intake and energy expenditure.
The brain takes:
- Neural
- Behavioral
- Hormonal
responses to maintain glucode uptake.
Code Review
Last edited: August 8, 2025A Code Review is a systematic study code by others—like proofreading an essay. There’s a few different ways of doing Code Review.
Why do we code review?
- catch bugs, style deviations, design + convention violations
- security trade-off: having someone who is well-versed in security is useful
- to know how other people’s code work
- to learn additional skills, languages, frameworks
Code Review Methodology
Don’t do it
- Very fast!
- None of the benefits of code review
Over-the-Shoulder Code Review
Over-the-Shoulder Code Review typically is done over someone’s shoulder—author walking the reviewer through code.
coherence time
Last edited: August 8, 2025The time it takes for a qubit to oscillate between two states between damping down.
cold sites
Last edited: August 8, 2025A family wide between SARS-COV2 variances identified specific sites which are maintained across variance of concerns suggesting why specific antibidies targeting them maybe able to render higher neutralizing potential
