Convex Problem Hiearchy
Last edited: January 1, 2026A Linear Program is equivalent to an SDP
cornucopia of analysis
Last edited: January 1, 2026Pythagorean Theorem
\begin{equation} \|u + v\|^{2} = \|u \|^{2} + \|v\|^{2} \end{equation}
if \(v\) and \(u\) are orthogonal vectors.
Proof:
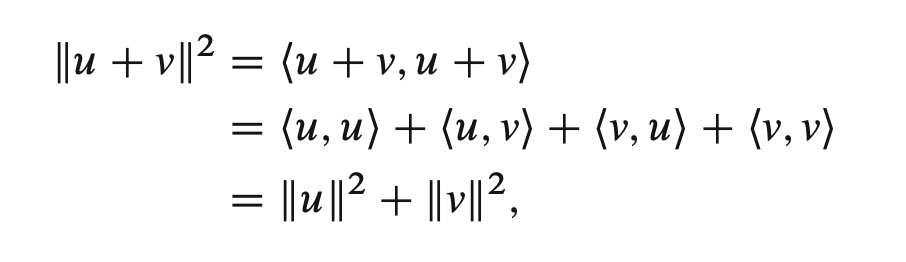
An Useful Orthogonal Decomposition
Suppose we have a vector \(u\), and another \(v\), both belonging to \(V\). We can decompose \(u\) as a sum of two vectors given a choice of \(v\): one a scalar multiple of \(v\), and another orthogonal to \(v\).
That is: we can write \(u = cv + w\), where \(c \in \mathbb{F}\) and \(w \in V\), such that \(\langle w,v \rangle = 0\).
Linear Constraint Optimization
Last edited: January 1, 2026\begin{align} \min_{x}\ &c^{\top} x + d \\ s.t.\ &Gx \preceq h \\ & Ax = b \end{align}
- linear objective function
- linear constraints
single our inequality forms a half-space; the entire feasible set is denoted by a series of linear functions—-these linear equalities are each CONVEX. The resulting feasible set, then, is ALSO convex—-meaning any line within the set remains within the set. So, any local minimum is a global minimum.
This is a convex problem where all constrains and objectives are affine.
More Convex Problems
Last edited: January 1, 2026Quadratically constrained quadratic program
Quadratic Program with quadratic constraints
Second-order cone programming
\begin{align} &\min f^{T} x \\ &s.t\ \norm{A_{i} x + b_{i}}_{2} \leq c_{i}^{T} x + d_{i}, i = 1 \dots m\\ & Fx = g \end{align}
Most things reduce down to a SOCP.
operations that preserve fuction convexity
Last edited: January 1, 2026- non-negative scaling
- sum: \(f_{1}+ f_{2}\) is convex if \(f_1, f_2\) is convex
- infinite sums: \(\sum_{i=1}^{\infty} f_{i}\) is convex
- integral: if \(f\qty(x,a)\) is convex in \(x\), \(\int_{a \in A} f\qty(x,a) \dd{a}\) is convex
- pre-composition with affine function: \(f\qty(Ax + b)\) is convex if \(f\) is convex
- pointwise maximum: \(f_{1}, …, f_{m}\) is convex, then \(f\qty(x) = \max \qty(f_{1} \qty(x)\dots f_n \qty(x))\) is convex
- supremum: if \(f\qty(x,y)\) is convex in \(x\) far each \(\text{sup}_{y \in Y} f\qty(x,y)\)
- partial minimization: \(f\qty(x) = \text{inf}_{y \in C} f\qty(x,y)\) (find the smallest value of \(f\) over \(y \in C\), or the point at which its approached)
- perspective of convex function is convex \(\text{persp}\qty(a,b) = b f\qty(\frac{a}{b})\)
- conjugate function of any function is convex
composition with scalar functions
\(g : \mathbb{R}^{n} \to \mathbb{R}\), \(h: \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}\), and let \(f = h\qty(g\qty(x)) = h \odot g\)
