controller
Last edited: August 8, 2025a controller is a that maintains its own state.
constituents
- \(X\): a set of nodes (hidden, internal states)
- \(\Psi(a|x)\): probability of taking an action
- \(\eta(x’|x,a,o)\) : transition probability between hidden states
requirements
Controllers are nice because we:
- don’t have to maintain a belief over time: we need an initial belief, and then we can create beliefs as we’d like without much worry
- controllers can be made shorter than conditional plans
additional information
finite state controller
A finite state controller has a finite amount of hidden internal state.
controller gradient ascent
Last edited: August 8, 2025We aim to solve for a fixed-sized controller based policy using gradient ascent. This is the unconstrained variation on PGA.
Recall that we seek to optimize, for some initial node \(x^{(1)}\) and belief-state \(b\), we want to find the distribution of actions and transitions \(\Psi\) and \(\eta\), which maximizes the utility we can obtain based on initial state:
\begin{equation} \sum_{s}b(s) U(x^{(1)}, s) \end{equation}
Recall that \(U(x,s)\) is given by:
\begin{equation} U(x, s) = \sum_{a}^{} \Psi(a|x) \qty[R(s,a) + \gamma \qty(\sum_{s’}^{} T(s’|s,a) \sum_{o}^{} O(o|a, s’) \sum_{x’}^{} \eta(x’|x,a,o) U(x’, s’)) ] \end{equation}
convolution
Last edited: August 8, 2025For \(f,g : \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{C}\), we have:
\begin{equation} (f * g)(x) = \int_{\mathbb{R}} f(x-y) g(y) \dd{y} = \int_{\mathbb{R}} f(y) g(x-y) \dd{y} \end{equation}
properties of convolution
- \((g * f) (x) = (f * g) (x)\)
- \(\mathcal{F}(f * g) = \mathcal{F}(f)\mathcal{F}(g)\)
- \(\mathcal{F}^{-1}(\hat{f} \hat{g}) = f * g\)
- \((f * g)’ = f * g’ = f’ * g\)
- \(\lambda ( f * g ) = (\lambda f) * g = f * (\lambda g)\)
=> “in a convolution, if ANY ONE of the two functions are Differentiable, both are Differentiable.”; think about smoothing a jagged function using a Gaussian.
Cook-Levin Theorem
Last edited: August 8, 2025Cook-Levin Theorem states that SAT and 3SAT are NP-complete. That is, for NP language \(L \in NP\), we have \(L \leq_{p} SAT\), meaning
exists a poly-computable function \(R: \qty {0,1}^{*} \to \qty {0,1}^{*}\) to perform the polynomial time mapping reduction \(x \to \phi_{x}\) such that:
\begin{equation} x \in L \Leftrightarrow R(x) = \phi_{x} \in \text{SAT} \end{equation}
\(3SAT \in NP\)
see 3cnf-formula
\(3SAT\) is \(NP\) hard
We will give a polynomial time mapping reduction.
For every string \(w\), we want to convert it to a 3cnf-formula such that \(w \in A \in NP\) IFF \(f(w) = \phi \in 3SAT\).
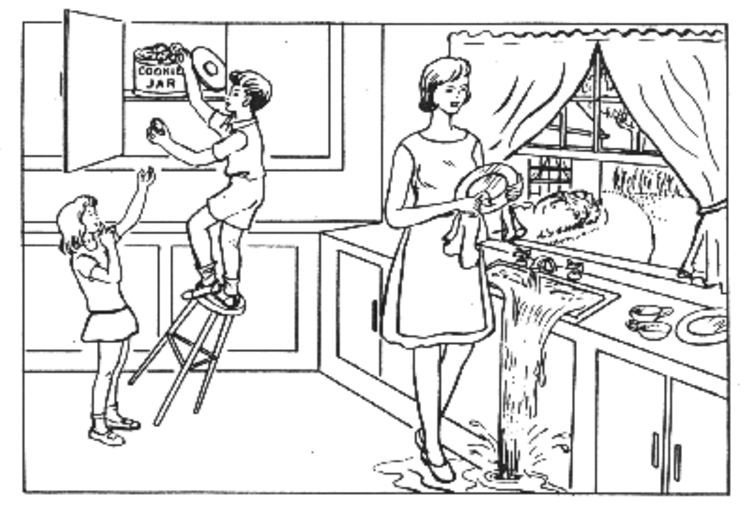
Cookie Theft Picture Description Task
Last edited: August 8, 2025Cookie Theft is a Discourse-Completion Task that involves describing the following picture: