Deontology
Last edited: January 1, 2026What duties do we owe and how should that shape our actions.
“truth telling” / “do no harm”
MOEReview Yun: Inference-Optimal MoEs
Last edited: January 1, 2026“the scaling law (Section 3) shows that more experts (larger E) result in a higher performance; on the other hand, more experts result in a larger inference cost (Section 4.2)”
How do we trade off cost of more experts (in terms of GPU-seconds or , for \(C_0\) being the cost for some per second GPU cost) and performance?
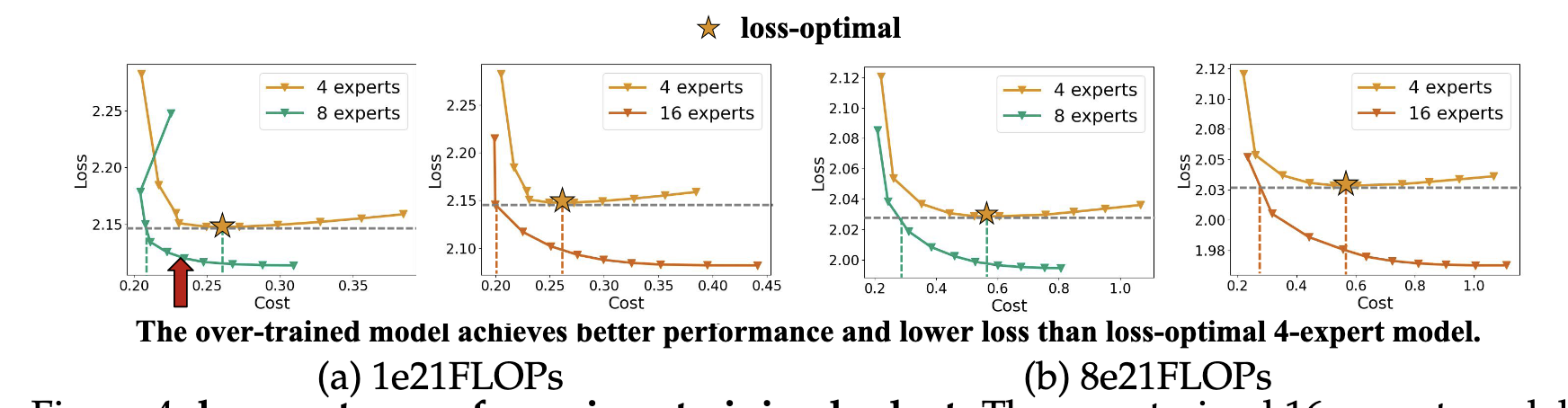
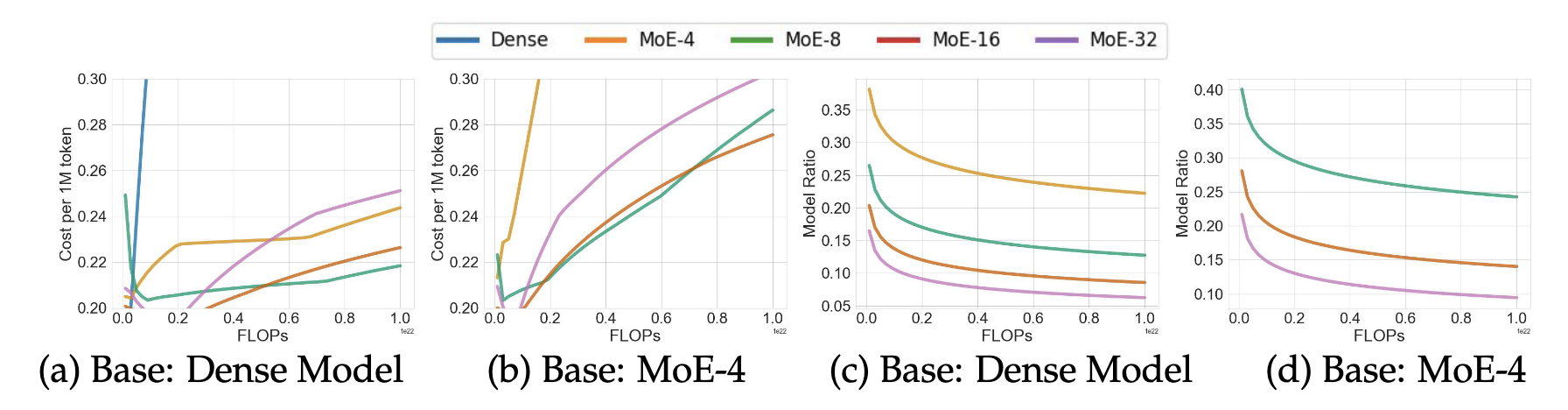
so, slight over-wraiting achieves better performance. Two findings:
- smaller bigger expert (4/8) is the most serving efficient, but costs more to train to the same loss
- with enough data, big (16/32) expert MoE could be smaller, and slight trianing can boost performance
non-linear optimization
Last edited: January 1, 2026Traditional techniques for non-convex problems involve compromises.
local optimization: find a point that minimize \(f_{0}\) among feasible points near it; can handle large problems (i.e. neural networks); algorithm parameter tuning.
global optimization methods: basically just cast it into a convex optimization problem.
optimization (programming languages)
Last edited: January 1, 2026optimization is a decision making method:
- identify a performance measure and a space of possible strategies to try
- run a bunch of simulations given a particular strategy, and measuring the performance
- try strategies with the goal of maximizing the performance measured
Importantly: model is not used to guide the search, it is only used to run simulations to evaluate performance.
Disadvantage (or advantage)
does not take a advantage of the structure of the problem
