Lyrics: Unnatural Exploration
Last edited: August 8, 2025Seed: explore, wild
explore
learn
resources
mineral
detail
feature
fact
police
duty
particulars
deposit
assign
undertake
natural
environment
cultivate
region
harshly
untrusting
nervous
increasing
changing
period
become greater
We go explore, changing times, parting ways.
Wanting no praise, become greater Than ever
We go explore, shining lights moving stars
Finding no target, we cannot expect to see
How can we explore if we can’t even feed? Ourselves? Our families? Our digitaries?
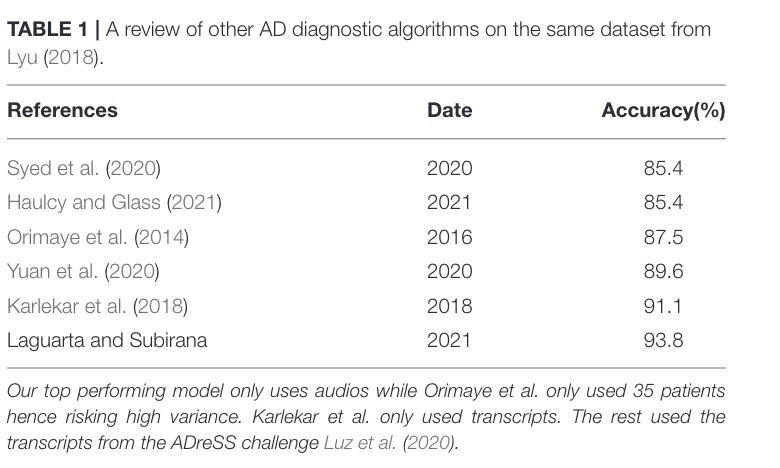
Lyu 2018
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2018.8633126
A dataset paper with which auditory info about people talking is collected.
Here are the state-of-the-art as of Laguarta 2021 on the dataset proposed.
machine learning
Last edited: August 8, 2025CS229: instead of solving a problem, learn from data to find a model to solve the problem approximately.
CS109: machine learning is the act of using some input to come up with some prediction, where the model is parameterized via a bunch of parameters. Hence, parameter learning approaches is how machine learning works.
CS205L: training data + model to estimate new data points with minimal error; the parallel is a “knowledge based system” with interpolation
macroaverage
Last edited: August 8, 2025For multi-class classification, the macroaverage is the average of statistical values (prec, recc, etc.) after they have been computed for each seperate class.
The microaverage is the combination of a confusion matrix BEFORE statistical values are computed.
magnetism
Last edited: August 8, 2025For a charge to do something in a magnetic field, it has to have velocity; nothing happens without movement.
So:
\begin{equation} \vec{F}_{M} = q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \end{equation}
To calculate: magnitude: \(qvB \sin \theta\) + right hand rule.
Radius
You maybe asked to find the radius of the path the particle takes, so:
\begin{equation} \frac{v^{2}}{r} = a \end{equation}
So, the net force here is:
\begin{equation} qvB = Ma \end{equation}
So plug in and solve
