MOEReview Krajewski: Scaling Laws for MoE
Last edited: December 12, 2025Define “granularity” as:
\begin{equation} G = \frac{d_{\text{ff}}}{d_{\text{expert}}} \end{equation}
at \(G=1\), we have a dense model; at \(G>1\), we have some kind of MoE.
Here are thy scaling laws:
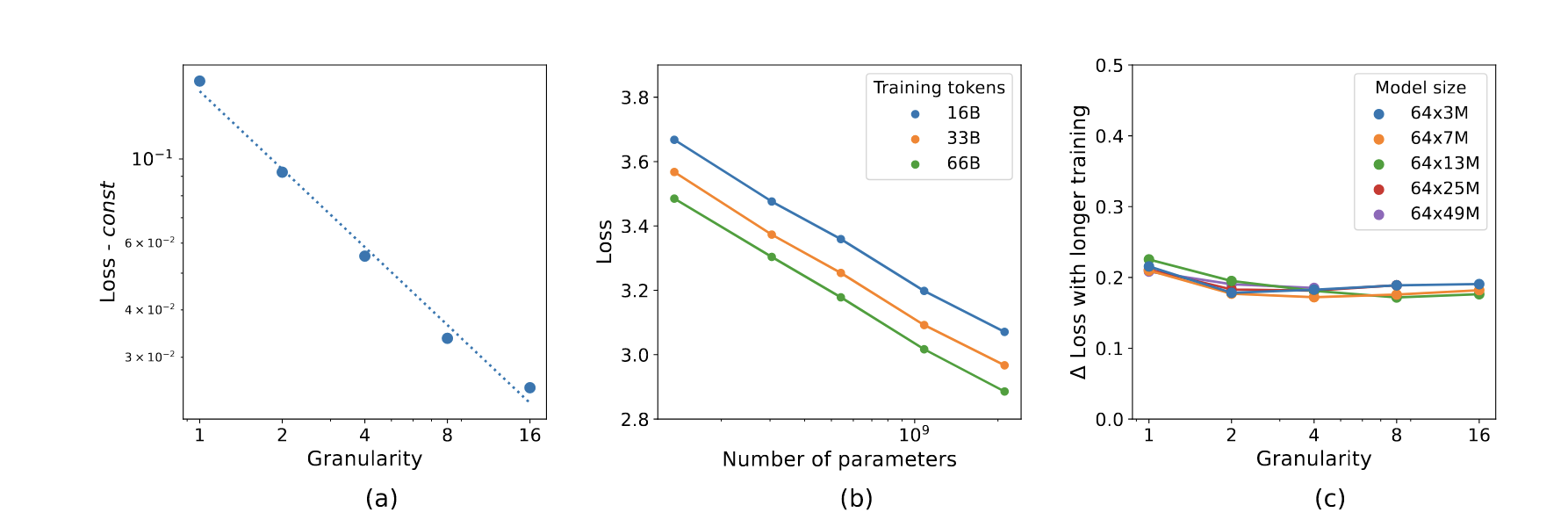
notice how its mostly linear! tiny experts yay!
MOEReview Li: Branch-Train-Merge
Last edited: December 12, 2025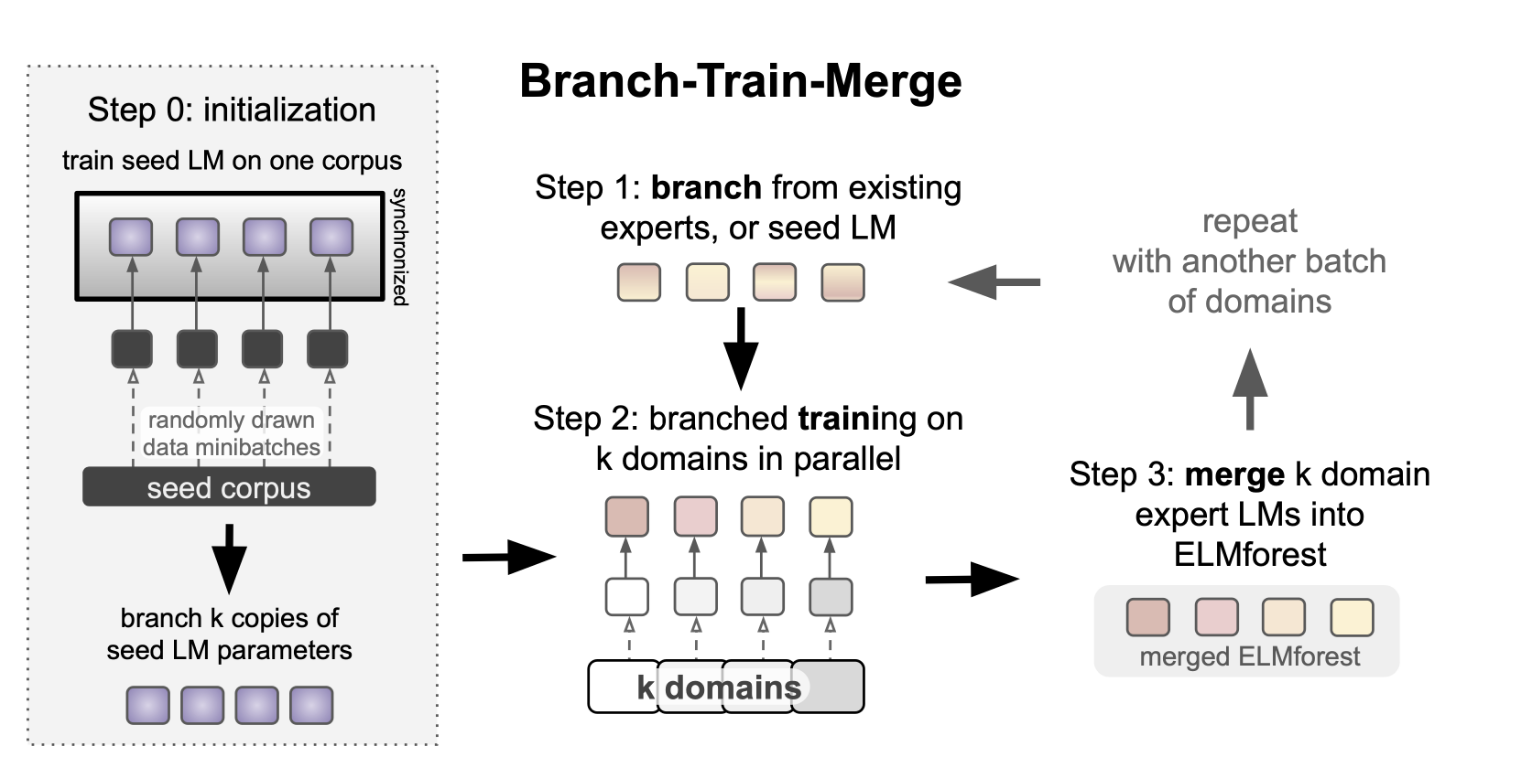
- weighted parameter average of the existing experts (or copy the new perts)
- training each expert independently
And then when inference we can use domain-conditioned averaging between the experts by computing:
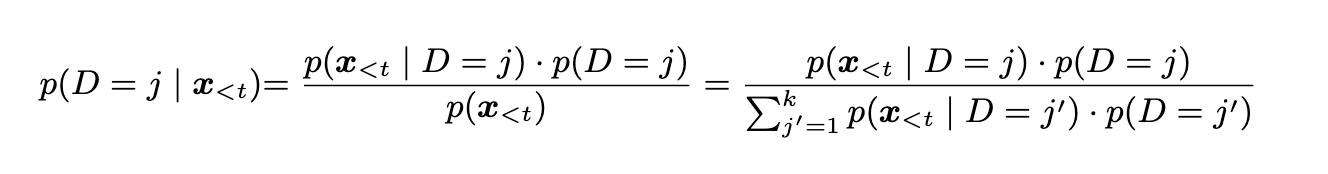
or by averaging the parameters of the experts.
MOEReview Pan: Dense Training Sparse Inference
Last edited: December 12, 2025Train experts densely, and then during inference keep only topk
MOEReview Rajbhandari: DeepSpeed MoE
Last edited: December 12, 2025Proposes: more MoEs at later layers + a shared expert.
MOEReview Sharma: LAZER
Last edited: December 12, 2025One-Liner
Getting rid of low singular value components in weights actually improves model performance.
Motivation
Previous work has shown that pruning SVD components works without significant performance degradation. But this work shows that with knowing where to prune more carefully, we can obtain better-than-baseline performance.
Notable Methods
We do this by trying all reductions based on \(\qty(\tau, \ell, \rho)\) tuples where we have \(\tau\) being the parameter type (projs q, k, v, attn out, mlp in and out), \(\ell\) being the layer number, and \(\rho\) being the rate of reduction.
