Partially Observable Markov Decision Process
Last edited: August 8, 2025Partially Observable Markov Decision Process is a with .
Components:
- states
- actions (given state)
- transition function (given state and actions)
- reward function
- Belief System
- beliefs
- observations
- observation model \(O(o|a,s’)\)
As always we desire to find a \(\pi\) such that we can:
\begin{equation} \underset{\pi \in \Pi}{\text{maximize}}\ \mathbb{E} \qty[ \sum_{t=0}^{\infty} \gamma^{t} R(b_{t}, \pi(b_{t}))] \end{equation}
whereby our \(\pi\) instead of taking in a state for input takes in a belief (over possible states) as input.
partially observable markov game
Last edited: August 8, 2025A markov game with State Uncertainty solved using POMDPs.
Parvin 2020
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.605317
One-Liner
An excercize scheme has had some measured effect on theta/alpha ratio and Brain wave frequency on AD patients; prognosis of AD not controlled for.
Novelty
- Leveraged physical training scheme and measured EEG effects by quantifying theta/alpha ratio
Notable Methods
- Used theta/alpha ratio as assay for improvement, and found the exercise scheme did so p<0.05
- Only tested patients with AD w/o a control for stage
Key Figs
Figure 1
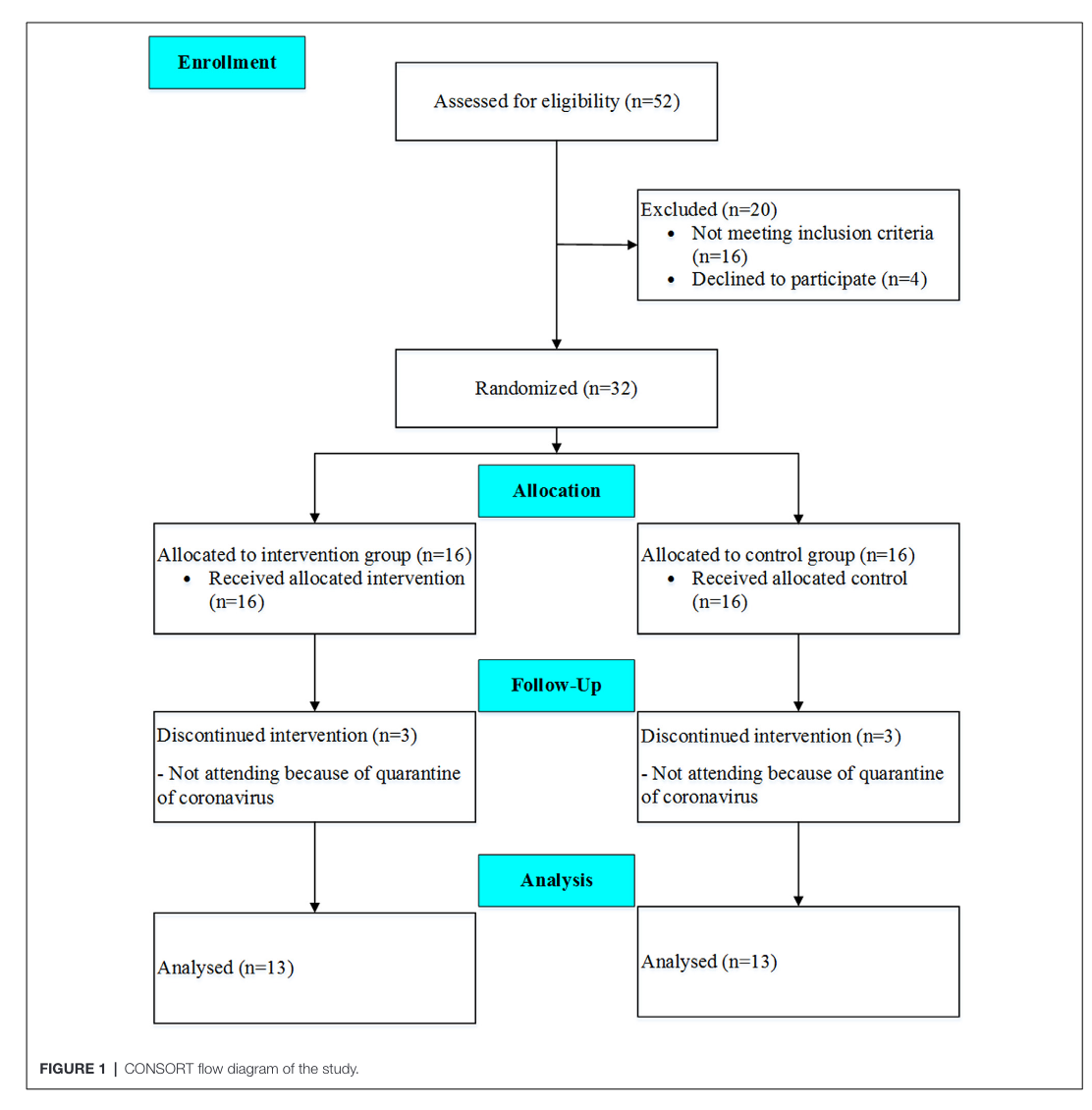
This figure tells us th N number of participants through the study
Patient Risk Prediction
Last edited: August 8, 2025Patient Scoring Systems
How do we score the status of a patient? Well, we can begin by having a chart—SpO2, can breath, etc. etc.
Drawbacks:
- these systems are quite generic
- not very representative of some information
Method
- MIMIC-IV 6000 ICU patient stays, 48994 vital signs—measuring across patient stays
- dynamic time warping to create a similar matrix
- clustering post-hoc to correlate patients together
PCP April Checkin
Last edited: August 8, 2025- No Demo Day
- TODO Email need statement template
Needfinding
- Not all patients want to be treated the same way
- Attitudes towards heathcare system
- Fostering strong interaction; facilitate interaction
Problem: patients have attitudes that physicians can’t effectively communicate.
Action item: interview doctors and patients
Need two need statement.
