Anna's Team Checkin
Last edited: August 8, 2025Need-finding conversation
Main idea: testing?—pregnancy testing and COVID testing
- talking to longer-scope challenges in visually impaired community
- Navigation; transportation
- Cannot see markers on smaller steps; trying to find an uber drive and cannot reorient
anotehuaoeu
Last edited: August 8, 2025Anoushka Krishnan
Last edited: August 8, 2025Anoushka is a student at Nueva, also the host of Project80, among other things.
Anthony Badger
Last edited: August 8, 2025Antonsson 2021
Last edited: August 8, 2025DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.607449
One-Liner
oral lexical retrieval works better than qualitative narrative analysis to classify dementia; and semantic fluency + Disfluency features chucked on an SVM returns pretty good results.
Novelty
Tried two different assays of measuring linguistic ability: oral lexical retrieval metrics, and qualitative discourse features analysis of speech.
Notable Methods
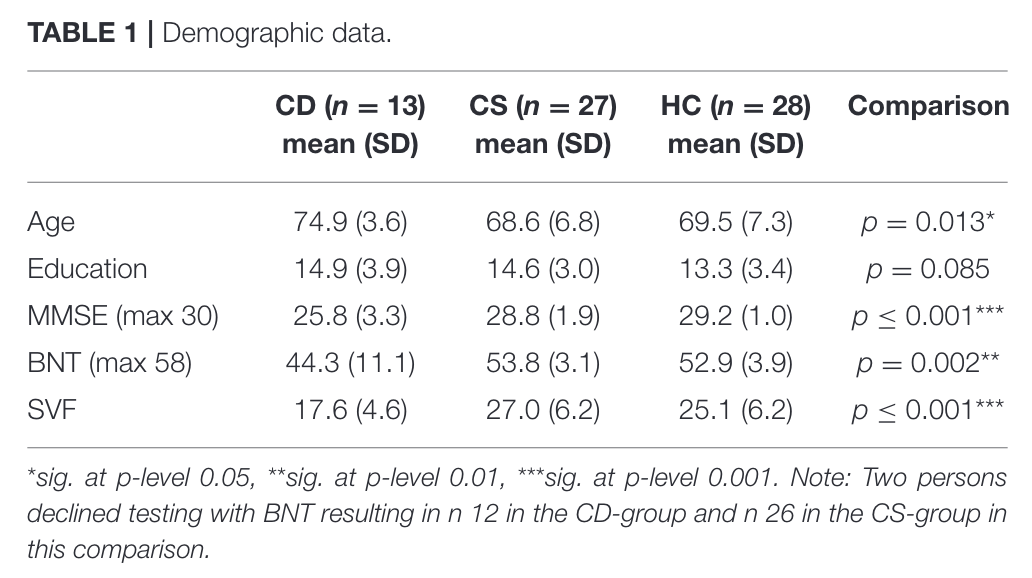
Subjects divided into three groups
- Great cog. decline
- Impaired but stable
- Healthy controls
Administered BNT and SVF tests as baseline
Key Figs
Table 3
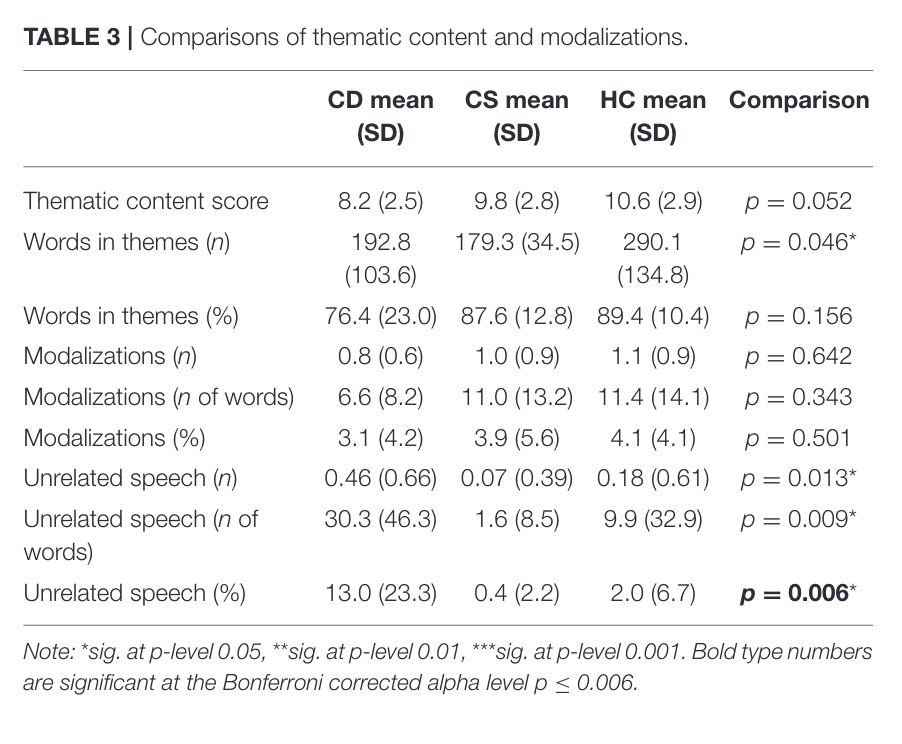
This figure tells us that the percentages of unrelated utterances was a statistically significant metric to figure differences between the three experimental groups.
