Bayes Normalization Constant
Last edited: August 8, 2025For some Baysian Network situation, you will note that there’s some bodge of values below:
\begin{equation} P(A|M) = \frac{P(M|A)P(A)}{P(M)} \end{equation}
if we are only interested in a function in terms of different values of \(a\), \(P(M)\) is not that interesting. Therefore, we can just calculate \(A\) for all \(a\), and then normalize it to sum to 1:
\begin{equation} P(A|M) \propto P(M|A)P(A) \end{equation}
and then, after calculating each \(P(M|A)P(A)\) , we just ensure that each thing sums to one.
Bayes Theorem
Last edited: August 8, 2025\begin{align} p(x\mid y) = \frac{p(y \mid x) p(x)}{p(y)} \end{align}
this is a direct result of the probability chain rule.
Typically, we name \(p(y|x)\) the “likelihood”, \(p(x)\) the “prior”.
Better normalization
What if you don’t fully know \(p(y)\), say it was parameterized over \(x\)?
\begin{align} p(x|y) &= \frac{p(y|x) \cdot p(x)}{p(y)} \\ &= \frac{p(y|x) \cdot p(x)}{\sum_{X_{i}} p(y|X_{i})} \end{align}
just apply law of total probability! taad
Bayes Theorem Over Random Variable
Last edited: August 8, 2025\begin{equation} P(B=b | D=d) = P(D=d|B=b) P(B=b) k \end{equation}
where, \(P(B=b | D=d)\) is your “posterior”; \(P(D=d|B=b)\) is your likelyhood; and \(P(B=b)\) is your prior.
Baysian Network
Last edited: August 8, 2025A Baysian Network is composed of:
- a directed, acyclic graph
- a set of conditional probabilities acting as factors.
You generally want arrows to go in the direction of causality.
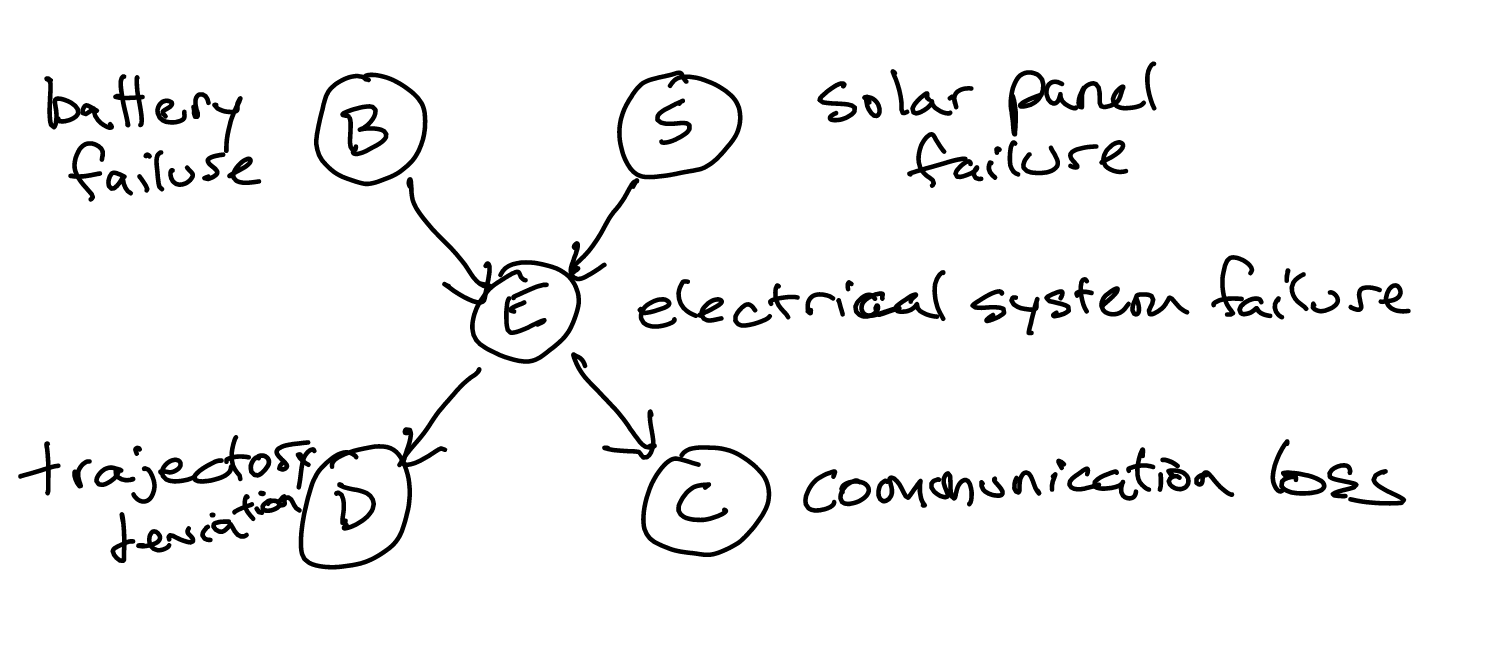
Via the chain rule of Bayes nets, we can write this equivalently as:
\begin{equation} (P(B) \cdot P(S)) \cdot P(E \mid B,S) \cdot P(D \mid E) \cdot P(C \mid E) \end{equation}
generally, for \(n\) different variables,
\begin{equation} \prod_{i=1}^{n} p(X_{i} \mid pa(x_{i})) \end{equation}
where, \(pa(x_{i})\) are the parent values of \(x_{i}\).
Baysian Networks for Healthcare
Last edited: August 8, 2025Representing conditional dependencies.
Semiparametric Expert Bayes Net
We use a Semiparametric Expert Bayes Net to learn the structure of the dynamics…. of medicine somewhere?
Atienza et al. 2022
- learns semiparemetic relations in expert basian networks
- uses gaussian rocesses for modeling no-linear performances + horseshoe regularization
2401.16419
Results
UCI Liver Disorder Dataste
- what is the oracle graph?
- what specific dynamics did the model learn?
