bloch sphere
Last edited: August 8, 2025The bloch sphere is a sphere encoding all possible probabilities of a qubit shared between two axis, \(|u\big>\) and \(|d\big>\).
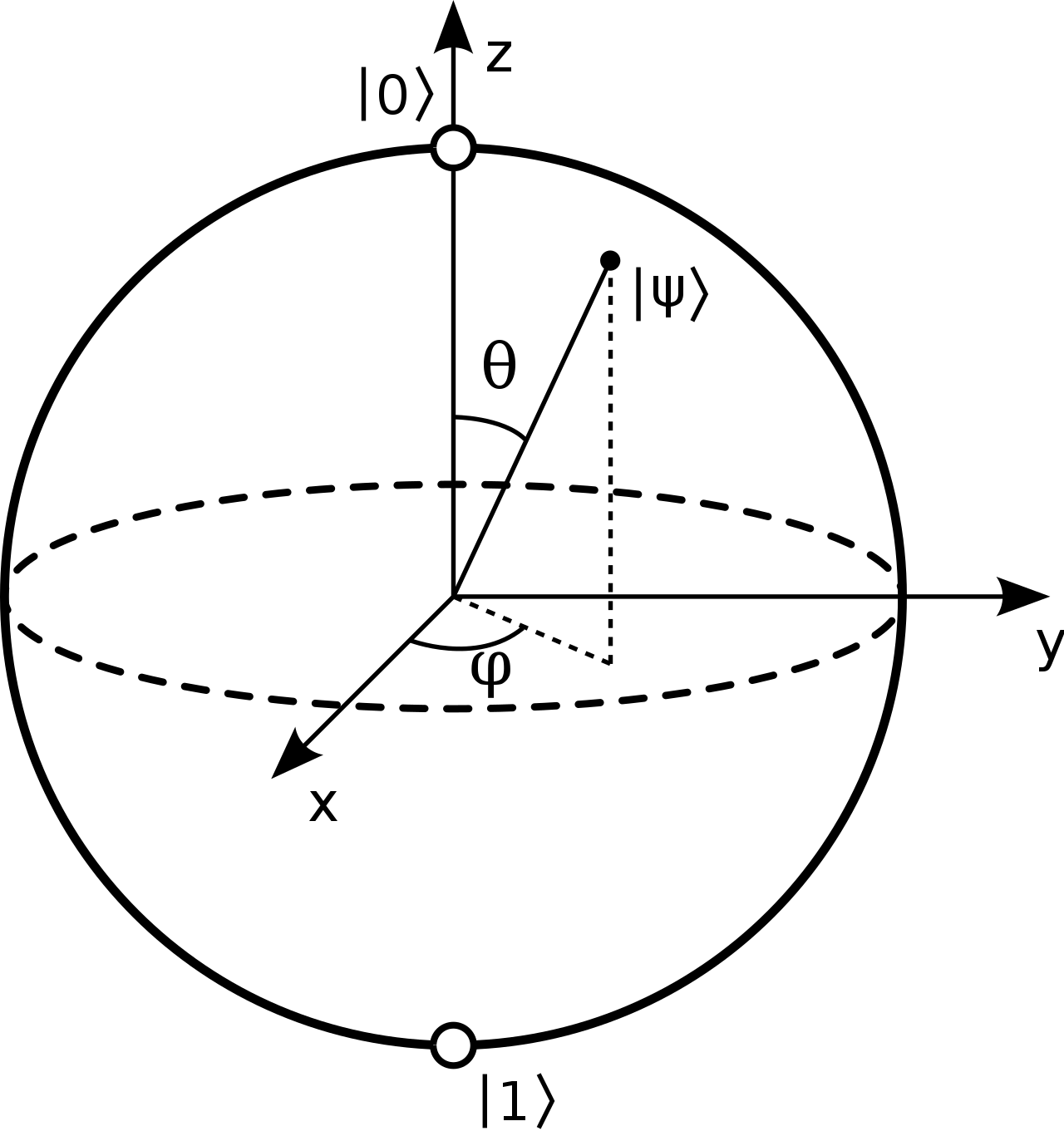
You will notice that its a unit sphere, in which any magnitude has size \(1\). Hence, probabilities would result as projected onto each of the directions.
Bluest Eye
Last edited: August 8, 2025Bluest Eye Essay Planning
Last edited: August 8, 2025General Information
| Due Date | Topic | Important Documents |
|---|---|---|
| Bluest Eye Essay | Bluest Eye |
Prompt
Beauty: discuss Morrison’s treatment of the idea of beauty. From what, where, or whom does this notion come? What effect does it have on the way one perceives the world? On the way others perceive an individual?
How does beauty (the acquisition of it, the lack of it, or the presence of it) determine one’s fate in America? Is beauty a necessarily fixed entity or does it fluctuate at the whim of society? How much or to what extent does one’s perception of beauty contribute to one’s sense of self-worth?
Bluest Eye: secondary source comparison activity
Last edited: August 8, 2025A secondary source comparison activity for the Bluest Eye
Tony Morrison’s Rootedness
That, if an action were to be done as in a community, its regarded as safer
It is a very personal grief and a personal statement done among people you trust. Done within the context of the community, therefore safe.
Public (white-washed) and private image, by necessesity, is separated
it’s just important that it be private. And then, whatever I do that is public can be done seriously.
